At WiseGEEK, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are the Causes of an Eye Migraine?
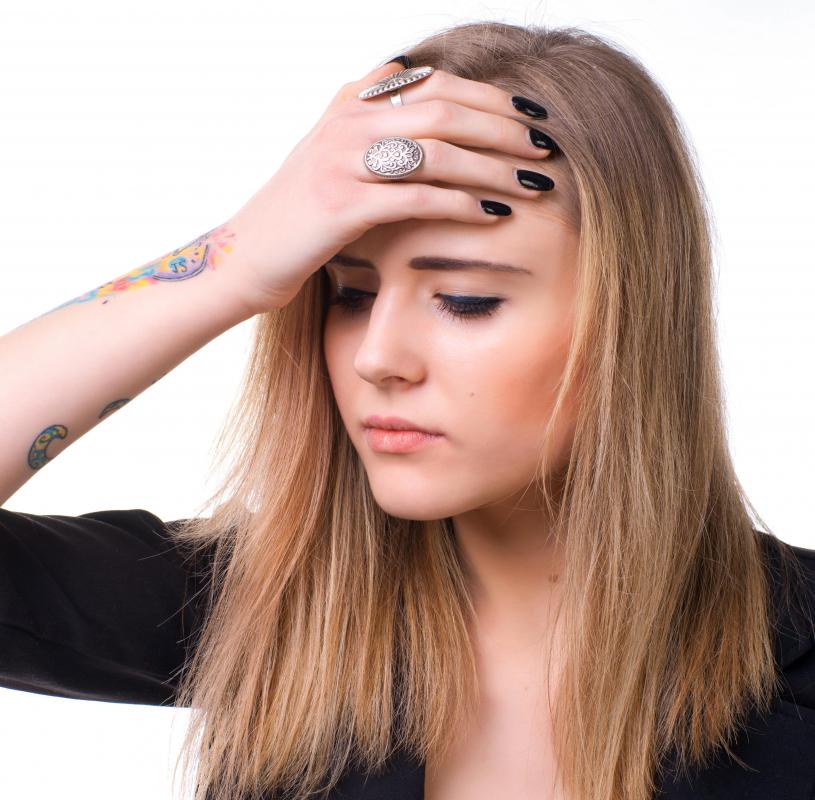
Many individuals feel crippled by the pain of migraine headaches. On occasion, a more alarming — but generally less serious — type of migraine may occur: the ocular migraine, or eye migraine. Identifiable more by their effects on a person's sense of sight than a sense of pain, eye migraines typically result from a disturbance in the areas of the brain responsible for vision. Body or environmental triggers may facilitate this disturbance.
Eye migraines represent a classification of migraine headache, yet some symptoms are unique to this particular condition. While the intense head pain, dizziness, and nausea associated with a traditional migraine may be a precursor of ocular headaches, the attack may also occur in the absence of any pain. In fact, a majority of ocular migraines produce no pain.

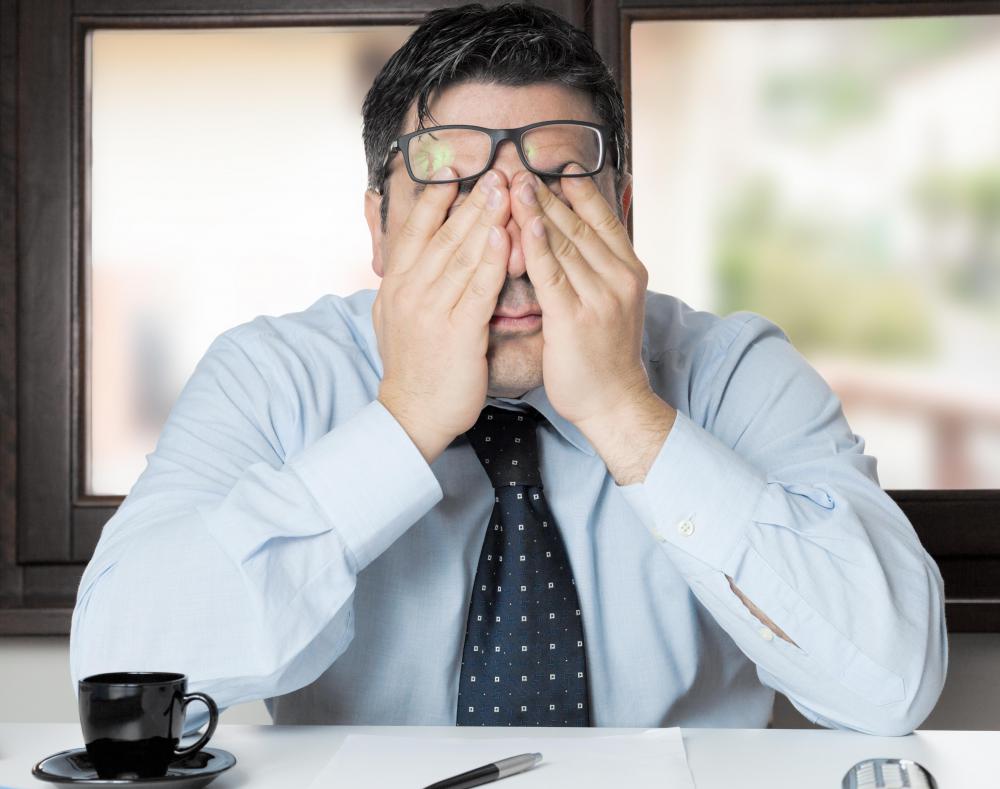
The primary feature of an eye migraine is a sudden visual distortion. Pupils will likely expand and the eyes may twitch, signaling an oncoming attack. An aura of hazy grayness or double vision may be present, but the most telling signal is a blind spot. This area of no vision grows and may be accompanied by flashing lights or jagged strobes, and blindness may even temporarily take hold in one eye. Although frightening, these episodes typically last less than 30 minutes.

A migraine is typically triggered when one’s brain and nervous system responds abnormally to specific stimulators. Some common migraine facilitators include flashing lights, medications, certain foods such as caffeine and cheese, and hormonal alterations in the body. Stress and fatigue can also create conditions for a migraine.
Once a migraine has begun, it often changes the rate of blood flow to the brain. When blood flow to the vision-producing occipital lobe or visual cortex is disrupted, an eye migraine may result. The visual symptoms of an ocular headache thus occur due to abnormal activity in the brain.

Another associated cause for eye migraines has been proposed: vasospasm. This condition happens when blood vessels tighten and spasm. If the action occurs in the visual areas of the brain, the visual disturbances related to an eye migraine could arise. A malfunction in the release of the brain chemical neurotransmitter serotonin may also cause vasoplasm.

Some individuals confuse ocular migraines with retinal migraines. In the latter serious condition, blood vessel tightening occurs in the areas leading to the eye's retina and optic nerve. Severe nausea and light sensitivity often coincide with these attacks — features not typically found in ocular migraines. Sustained retinal migraines, unlike ocular migraines, may eventually lead to permanent visual damage.

Since an average eye migraine is technically a brain dysfunction and not a disorder of the eye itself, treatment is more difficult, and in most cases the symptoms will cease with time. Usual headache remedies like aspirin may help alleviate any associated pain. As for ocular headache treatment for troublesome visual disturbances, prescribed medications could be of assistance in persistent cases. Some research suggests that B vitamins and folic acid reduce migraine symptoms in many individuals. If one is performing a task that requires sound vision, the safest course of action is to cease that task until the eye migraine attack has ended.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discuss this Article
Post your comments